Research & Discovery
From There to Hear: Locating Sound Distance
Researchers at UConn Health have identified the mechanisms by which rabbits and humans recognize the distance of sound from its origin to the listener.
April 2, 2015 | Kim Krieger
Autism Recovery – Questioning the Impossible
Research by UConn psychology professor Deborah Fein suggests that some children with autism can overcome the symptoms over time and with intense therapy.
April 2, 2015 | Angelina Reyes
Plants Aren’t in Lockstep When Responding to Environmental Changes
A UConn study shows that trait diversity in plants may result from individual responses to the environment, rather than – as is often assumed – being uniform across species.
March 31, 2015 | Sheila Foran
Smartphone App Could Change How Depression is Diagnosed
The app, developed by UConn researchers, collects data on behavior signs that indicate depression.
March 30, 2015 | William Weir, School of Engineering
Physicists Solve Low-Temperature Magnetic Mystery
A breakthrough in explaining a rare property of an exotic magnetic material could lead to new technologies, from information storage to magnetic refrigeration.
March 26, 2015 | Tim Miller
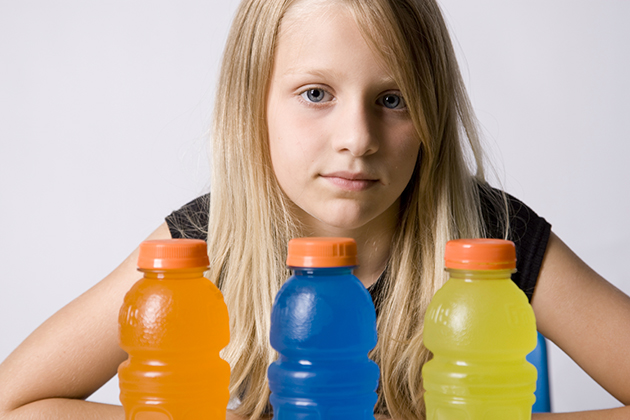
Children and Energy Drinks: A Growing Public Health Crisis
A new study shows that highly-caffeinated, often sugar-laden energy drinks can harm children and adolescents, and supports calls for restrictions.
March 24, 2015 | Daniel P. Jones, Rudd Center
Passion for Art May Thwart Pursuits of the Heart
Individuals who share their creativity with their partner are more likely to enjoy long-term relationships, but solo pursuits may keep them single, according to a new UConn study.
March 17, 2015 | Colin Poitras
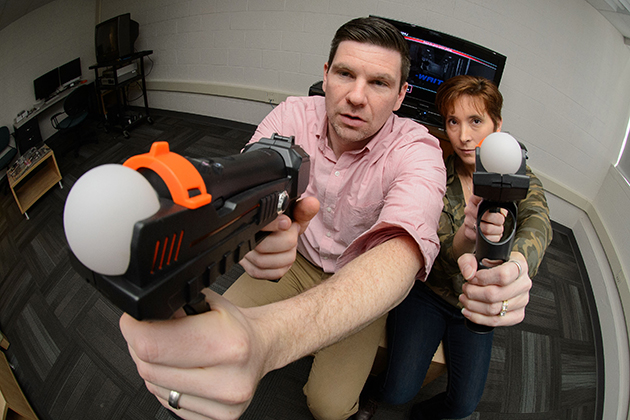
Realistic Gun Controllers in Video Games Foster Aggressive Thoughts
Players who used a gun controller also found the game more realistic, and felt more engaged, according to a new UConn study.
March 16, 2015 | Sheila Foran
Diabetes Drug Shown Not to Increase Heart Failure Risk
The study, published in The Lancet, is based on data from a global clinical trial led by a UConn Health physician-researcher.
March 12, 2015 | Christopher DeFrancesco '95 (CLAS)
Parents Misled by Marketing of ‘Healthy’ Drinks, Study Says
Nutritional claims on packaging, such as the use of terms such as 'real,' 'natural,' 'containing vitamin C,' 'antioxidants,' and 'low in calories,' are important factors in parents' purchasing decisions.
March 11, 2015 | Daniel P. Jones, Rudd Center